Configuring SNMP Security
There is no specific command that you use to enable SNMP. To configure SNMP support, perform the tasks described in the following steps, only the first two steps are mandatory:
1.Enable the SNMP community string to define the relationship between the network
management station and the agent with the following command:
snmp−server community
The number value references an optional access−list.
2.Use this command to configure the router to send traps to an NMS host:
snmp−server host host [version {1|2c}]
3.Configure the type of traps for which a notification is sent to the NMS. You do so with the following command:
snmp−server enable traps [notification type] –
[notification option]
4.Set the system contact, location, and serial number. You can set the systems contact with the snmp−server contact [text] command. You set the location with the snmp−server location [text] command, and you set the serial number with the snmp−server chassis−id [text] command.
5.Use the access−list command to specify a list of hosts that are allowed read−, read/write, or write−only access to the router.
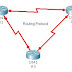
The picture below: shows Router 1, which is configured to allow SNMP read−only access and read/write access from two separate hosts. Router 1 is also configured to send SNMP trap information to the same two hosts. The following lines show how Router 1 should be configured so SNMP access from both host 192.168.10.1 and 192.168.10.2 is allowed and SNMP trap information is sent to both hosts:access−list 12 permit 192.168.10.1
access−list 13 permit 192.168.10.2
snmp−server contact VISA
snmp−server location Network Engineers
snmp−server chassis−id 200000444
snmp−server community observe RO 12
snmp−server community adjust RW 13
snmp−server host 192.168.10.1 observe snmp
snmp−server host 192.168.10.2 adjust snmp